- Home
- About Us
-
Products & Services
Hydroxyethyl methacrylate(HEMA)Hydroxypropyl methacrylate (HPMA)Hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA)Hydroxypropyl acrylate(HPA)Methacrylic acid(MAA)lsobornyl acrylate(IBOA)Methyl methacrylate (MMA)lsobornyl methacrylate(IBOMA)P-Phenylenediamine(PPD) 4-Nitroaniline(PNA)Expandable MMA beadsEthyl Methyl Carbonate(EMC)Barrel industry products
- Application
- News
- Honor
- Factory
- Contact Us
- HomeHome
- About UsAbout Us
- Products & ServicesProducts & Services
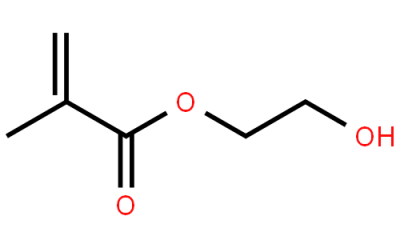
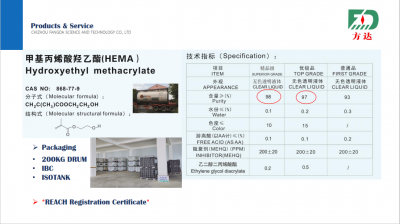
- Hydroxyethyl methacrylate(HEMA)
- Hydroxypropyl methacrylate (HPMA)
- Hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA)
- Hydroxypropyl acrylate(HPA)
- Methacrylic acid(MAA)
- lsobornyl acrylate(IBOA)
- Methyl methacrylate (MMA)
- lsobornyl methacrylate(IBOMA)
- P-Phenylenediamine(PPD)
- 4-Nitroaniline(PNA)
- Expandable MMA beads
- Ethyl Methyl Carbonate(EMC)
- Barrel industry products
- ApplicationApplication
- NewsNews
- HonorHonor
- FactoryStyle
- Contact UsContact Us
- 中文版
Fangda Chemical
Dedicated to producing new chemical materials
Fangda Chemical
Improve testing equipment and advanced production processes
Fangda Chemical
Pioneering · enterprising · innovative · pragmatic
Down
Hydroxyl monomer specialists, hand in hand with you for the future!
The company invested and built Chizhou Fangda Technology Co., Ltd. in October 2006, which is a national high-tech enterprise specializing.
-
66600m2
Factory footprint
-
2000
Quzhou Fangda Chemical was established in
-
70000mt
Annual output
The company mainly produces methacrylic acid, hydroxyethyl acrylate, hydroxypropyl acrylate, hydroxyethyl methacrylate, hydroxypropyl methacrylate, isobornyl methacrylate.
The first time to learn more about the latest news of Fonda Chemical, we will be happy to serve you!